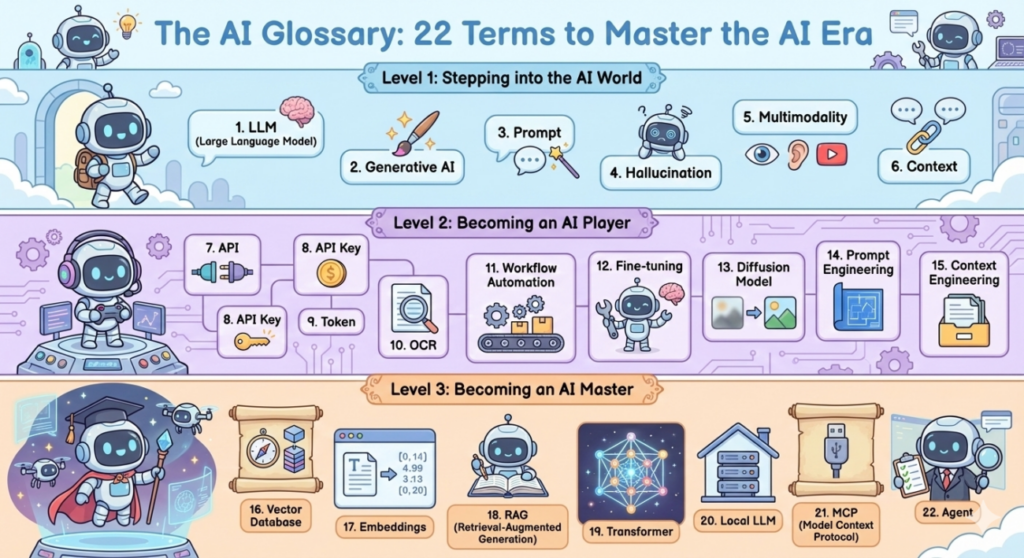
Welcome back to learnwithandric. As I build my AI projects and automate financial workflows, I’ve realized that understanding the “language of AI” is the first step to mastery. Here is a breakdown of 22 essential terms, categorized into three levels to help you go from a beginner to an AI master.
Level 1: Stepping into the AI World
1. LLM (Large Language Model)
- The “brain” behind tools like ChatGPT. It is trained on massive amounts of data to understand and generate human-like text.
- Example: When you ask ChatGPT for a stock summary, it uses an LLM to process your request.
2. Generative AI
- AI that can “create” new things, including text, images, music, or even video.
- Example: Using Midjourney to create a professional header image for your blog.
3. Prompt
- The instructions or “spells” you give to the AI.
- Example: “Act as a financial advisor and analyze this annual report.”
4. Hallucination
- When AI confidently makes up facts or nonsensical information.
- Example: An AI citing a non-existent tax law during a financial simulation.
5. Multimodality
- The ability of AI to understand more than just text, such as images, audio, and video.
- Example: Uploading a screenshot of a stock chart and asking AI to explain the trend.
6. Context
- The “short-term memory” of AI within a single conversation.
- Example: If you mention “Apple” earlier in the chat, the AI knows you mean the company, not the fruit, in the next sentence.
Level 2: Becoming an AI Player
7. API (Application Programming Interface)
- A “universal socket” that allows different software to talk to each other.
- Example: Using an API to connect your stock price tracker to n8n.
8. API Key
- A unique password used to access and pay for specific API services.
- Example: Your secret key for OpenAI that allows n8n to generate text.
9. Token
- The basic unit used to measure AI usage; roughly equivalent to syllables or words.
- Example: A 500-word essay might cost around 700 tokens to generate.
10. OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
- Technology that allows computers to “read” text inside images.
- Example: Scanning a physical receipt so n8n can log the data into Excel.
11. Workflow Automation
- Setting up a series of tasks for different tools to complete automatically.
- Example: When a new email arrives, AI summarizes it and sends a notification to LINE.
12. Fine-tuning
- Taking a general AI and training it with your own data to make it an expert in a specific field.
- Example: Training an AI on your 13 years of financial advisory notes to mimic your specific style.
13. Diffusion Model
- The core technology behind modern AI image generation.
- Example: Tools like Stable Diffusion that turn a blurry mess of pixels into a clear image.
14. Prompt Engineering
- The art of designing specific prompts to improve AI accuracy and reduce errors.
- Example: Using specific frameworks like “Role-Context-Task” to get better investment reports.
15. Context Engineering
- An advanced version of prompt engineering that focuses on how to present background info to the AI.
- Example: Organizing a client’s history neatly so the AI gives better financial advice.
Level 3: Becoming an AI Master
16. Vector Database
- A database that stores the “meaning” of data, making it easy to find similar information.
- Example: Storing hundreds of investment articles so you can search for “market trends” semantically.
17. Embeddings
- The process of turning text or images into a list of numbers that computers understand.
- Example: Converting a paragraph of financial advice into a numerical “coordinate” in a database.
18. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
- Forcing the AI to look at specific data sources (like your PDFs) before answering, preventing it from making things up.
- Example: Telling the AI: “Answer this based ONLY on the 2024 tax guide I uploaded.”
19. Transformer
- The underlying architecture of almost all modern LLMs; the “T” in GPT.
- Example: Think of it as a super-intelligent “reading comprehension master” that powers AI logic.
20. Local LLM
- Running an AI model directly on your own computer instead of the cloud to ensure privacy.
- Example: Using Ollama to run an AI that analyzes sensitive client data without it ever leaving your laptop.
21. MCP (Model Context Protocol)
- A “universal connector” or “USB-C” for AI, allowing different models to use the same tools.
- Example: A standard that lets both Claude and GPT use the same database of stock prices easily.
22. Agent
- An AI that can think, plan, and use tools independently to achieve a complex goal.
- Example: An “Investment Agent” that searches the web, analyzes a stock, and writes a report for you autonomously.
Which level are you at right now?
Let me know in the comments, and let’s grow together at learnwithandric!